Understanding Clause 1.15: Limitation of Liability in FIDIC Yellow Book 2017
Definition and Scope
Clause 1.15: Limitation of Liability outlines the limits on the liability of the Contractor and the Employer under the contract. This clause is crucial as it sets the boundaries for the financial and legal responsibilities of both parties, ensuring that neither party is exposed to unlimited liability.
Key Aspects
- Cap on Liability: The clause typically sets a maximum limit on the amount of liability that either party can incur. This cap is often expressed as a percentage of the contract price.
- Exclusions: Certain types of liabilities may be excluded from the limitation, such as liabilities arising from fraud, gross negligence, or willful misconduct1.
- Consequential Damages: The clause may also address the exclusion of consequential damages, which are indirect losses that occur as a result of a breach of contract.
Purpose
The primary purpose of Clause 1.15 is to provide a clear framework for the allocation of risk between the Contractor and the Employer. By setting limits on liability, the clause helps to protect both parties from excessive financial exposure and encourages a fair and balanced approach to risk management.
Example Scenarios
- Construction Delays: If the Contractor is responsible for a delay in the project, the Employer may seek damages.
Understanding Clause 1.15: Limitation of Liability in FIDIC Yellow Book 2017 Read More »














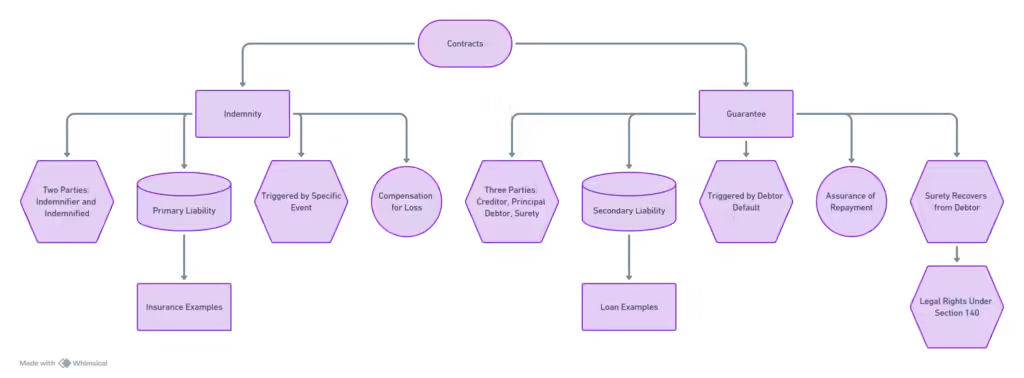
























![Sub-Clause 14.7 ["Payment"]](https://i0.wp.com/wisdomwaveshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/image-26.png?fit=1024%2C729&ssl=1)








![Flowchart Explaining CLAUSE 11.0 DEFECTS LIABILITY [FIDIC Yellow Book 1999]](https://i0.wp.com/wisdomwaveshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/image-4.png?fit=1024%2C539&ssl=1)



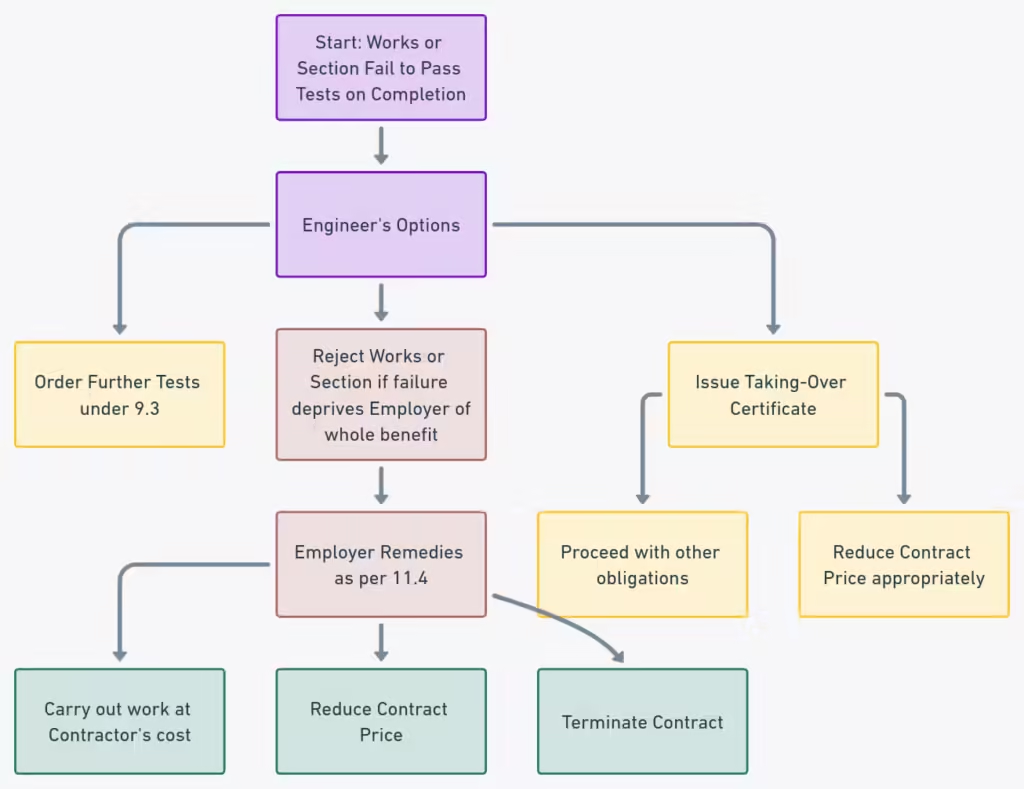
![Clause 9.4 Failure to Pass Tests on Completion [FIDIC Yellow Book 1999]](https://i0.wp.com/wisdomwaveshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/9.4.png?fit=1024%2C789&ssl=1)

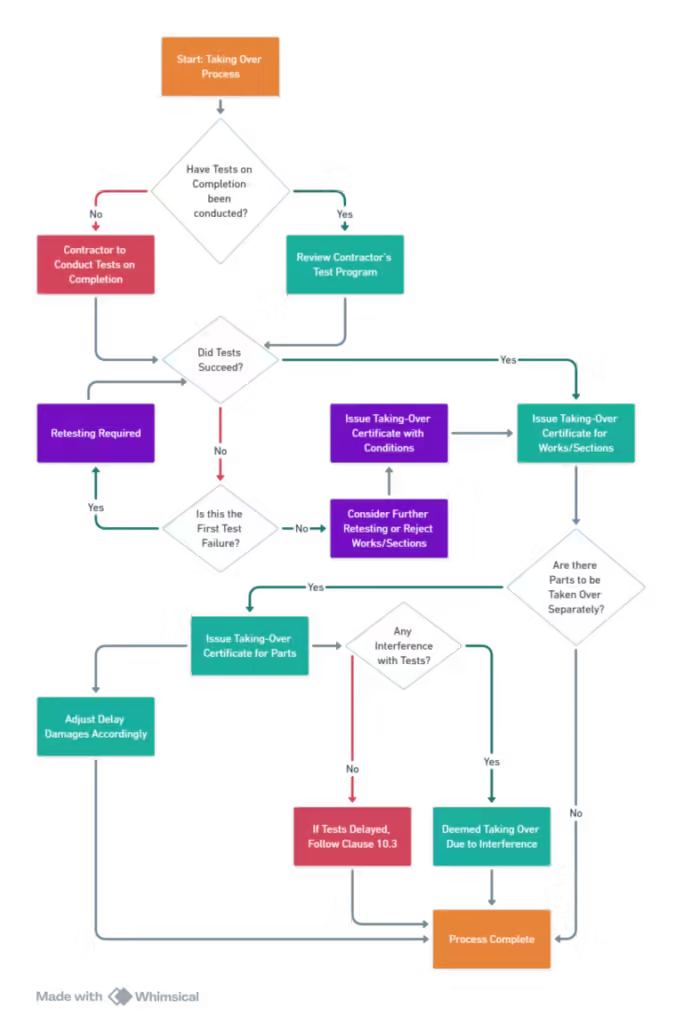
![Clause 10.0 EMPLOYER’S TAKING OVER [FIDIC Yellow Book 1999]](https://i0.wp.com/wisdomwaveshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Untitled.jpg?fit=543%2C1024&ssl=1)








